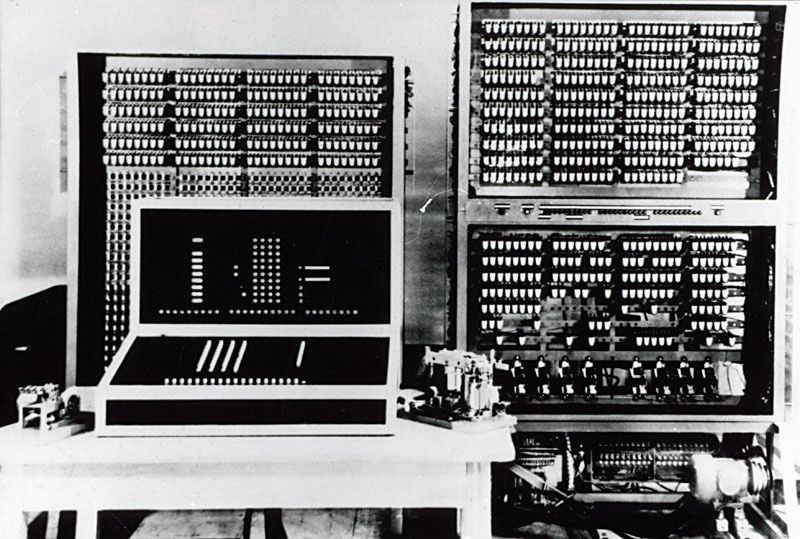
The Z3, an early computer built by German engineer Konrad Zuse working in complete isolation from developments elsewhere, uses 2,300 relays, performs floating point binary arithmetic, and has a 22-bit word length. The Z3 was used for aerodynamic calculations but was destroyed in a bombing raid on Berlin in late 1943. Zuse later supervised a reconstruction of the Z3 in the 1960s, which is currently on display at the Deutsches Museum in Munich.
Isaac Asimov publishes the science fiction short story Liar! in the May issue of Astounding Science Fiction. In it, he introduced the Three Laws of Robotics:
A robot may not injure a human being or, through inaction, allow a human being to come to harm.
A robot must obey the orders given to it by human beings, except where such orders would conflict with the First Law.
This is thought to be the first known use of the term “robotics.”
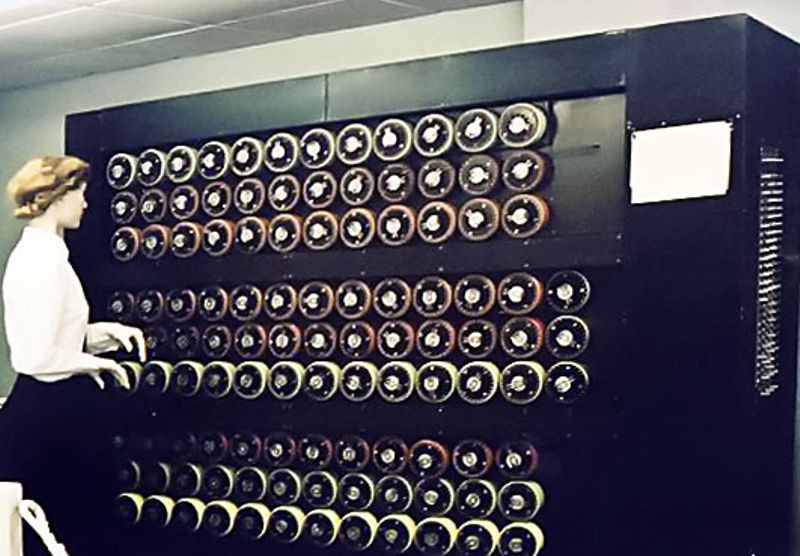
Built as an electro-mechanical means of decrypting Nazi ENIGMA-based military communications during World War II, the British Bombe is conceived of by computer pioneer Alan Turing and Harold Keen of the British Tabulating Machine Company. Hundreds of allied bombes were built in order to determine the daily rotor start positions of Enigma cipher machines, which in turn allowed the Allies to decrypt German messages. The basic idea for bombes came from Polish code-breaker Marian Rejewski's 1938 "Bomba."