Timeline
Pre-1940s
First Semiconductor Effect is Recorded
Michael Faraday describes the "extraordinary case" of his discovery of electrical conduction increasing with temperature in silver sulfide crystals. This is the opposite to that observed in copper and other metals.
Semiconductor Point-Contact Rectifier Effect is Discovered
In the first written description of a semiconductor diode, Ferdinand Braun notes that current flows freely in only one direction at the contact between a metal point and a galena crystal.
Semiconductor Rectifiers Patented as "Cat's Whisker" Detectors
Radio pioneer Jagadis Chandra Bose patents the use of a semiconductor crystal rectifier for detecting radio waves.
Field Effect Semiconductor Device Concepts Patented
Julius Lilienfeld files a patent describing a three-electrode amplifying device based on the semiconducting properties of copper sulfide. Attempts to build such a device continue through the 1930s.
"The Theory Of Electronic Semi-Conductors" is Published
Alan Wilson uses quantum mechanics to explain basic semiconductor properties. Seven years later Boris Davydov (USSR), Nevill Mott (UK), and Walter Schottky (Germany) independently explain rectification.
1940s
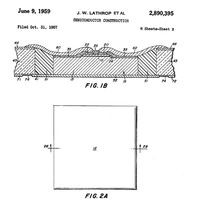
Discovery of the p-n Junction
Russell Ohl discovers the p-n junction and photovoltaic effects in silicon that lead to the development of junction transistors and solar cells.
Semiconductor diode rectifiers serve in WW II
Techniques for producing high purity germanium and silicon crystals are developed for wartime radar microwave detectors.
Invention of the Point-Contact Transistor
John Bardeen & Walter Brattain achieve transistor action in a germanium point-contact device in December 1947.
The European Transistor Invention
Herbert Mataré & Heinrich Welker independently create a germanium point-contact transistor in France.
Conception of the Junction Transistor
William Shockley conceives an improved transistor structure based on a theoretical understanding of the p-n junction effect.
1950s
Development of Zone Refining
William Pfann and Henry Theurer develop zone refining techniques for production of ultra-pure semiconductor materials.
First Grown-Junction Transistors Fabricated
Gordon Teal grows large single crystals of germanium and works with Morgan Sparks to fabricate an n-p-n junction transistor.
Transistorized Consumer Products Appear
Semiconductors appear in battery-powered hearing aids and pocket radios where consumers are willing to pay a premium for portability and low power consumption.
Bell Labs Licenses Transistor Technology
Bell Labs technology symposia and licensing of transistor patents encourages semiconductor development.
Transistorized Computers Emerge
A transistorized computer prototype demonstrates the small size and low-power advantages of semiconductors compared to vacuum tubes.
Diffusion Process Developed for Transistors
Following the production of solar cells using high-temperature diffusion methods, Charles Lee and Morris Tanenbaum apply the technique to fabricate high-speed transistors.
Silicon Transistors Offer Superior Operating Characteristics
Morris Tanenbaum fabricates the first silicon transistor at Bell Labs but Texas Instruments' engineers build and market the first commercial devices.
Photolithography Techniques Are Used to Make Silicon Devices
Jules Andrus and Walter Bond adapt photoengraving techniques from printing technology to enable precise etching of diffusion "windows" in silicon wafers.
Development of Oxide Masking
Carl Frosch and Lincoln Derick grow a silicon dioxide film on wafers to protect their surface and allow controlled diffusion into the underlying silicon.
Silicon Comes to Silicon Valley
Shockley Semiconductor Laboratory develops Northern California's first prototype silicon devices while training young engineers and scientists for the future Silicon Valley.
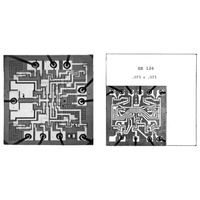
All Semiconductor "Solid Circuit" is Demonstrated
Jack Kilby produces a microcircuit with both active and passive components fabricated from semiconductor material.
Silicon Mesa Transistors Enter Commercial Production
Fairchild Semiconductor produces double-diffused silicon mesa transistors to meet demanding aerospace applications.
Tunnel Diode Promises a High-Speed Semiconductor Switch
Leo Esaki's novel device is an example of many celebrated semiconductor breakthroughs that do not sustain their early promise as they are overtaken by competing technologies.
Practical Monolithic Integrated Circuit Concept Patented
Robert Noyce builds on Jean Hoerni's planar process to patent a monolithic integrated circuit structure that can be manufactured in high volume.
Invention of the "Planar" Manufacturing Process
Jean Hoerni develops the planar process to solve reliability problems of the mesa transistor, thereby revolutionizing semiconductor manufacturing.
1960s
Epitaxial Deposition Process Enhances Transistor Performance
Development of thin-film crystal-growth process leads to transistors with high switching speeds.
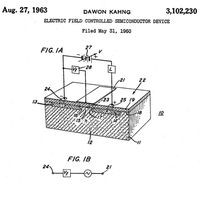
Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) Transistor Demonstrated
John Atalla and Dawon Kahng fabricate working transistors and demonstrate the first successful MOS field-effect amplifier.
First Planar Integrated Circuit is Fabricated
Jay Last leads development of the first commercial IC based on Hoerni's planar process and Noyce's monolithic approach.
Dedicated Semiconductor Test Equipment Enters Commercial Market
Semiconductor and independent vendors build dedicated test equipment for high-throughput manufacturing.
Silicon Transistor Exceeds Germanium Speed
Computer architect Seymour Cray funds development of the first silicon device to meet the performance demands of the world's fastest machine.
Aerospace systems are the first applications for ICs in computers
The size, weight, and reduced power consumption of integrated circuits compared to discrete transistor designs justify their higher cost in military and aerospace systems.
Standard Logic IC Families Introduced
Diode Transistor Logic (DTL) families create a high-volume market for digital ICs but speed, cost, and density advantages establish Transistor Transistor Logic (TTL) as the most popular standard logic configuration by the late 1960s.
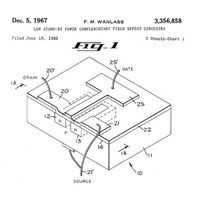
Complementary MOS Circuit Configuration is Invented
Frank Wanlass invents the lowest power logic configuration but performance limitations impede early acceptance of today's dominant manufacturing technology.
First Commercial MOS IC Introduced
General Microelectronics uses a Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (MOS) process to pack more transistors on a chip than bipolar ICs and builds the first calculator chip set using the technology.
The First Widely-Used Analog Integrated Circuit is Introduced
David Talbert and Robert Widlar at Fairchild kick-start a major industry sector by creating commercially successful ICs for analog applications.
Hybrid Microcircuits Reach Peak Production Volumes
Multi-chip SLT packaging technology developed for the IBM System/360 computer family enters mass production.
Semiconductor Read-Only-Memory Chips Appear
Semiconductor read-only-memories (ROMs) offer high density and low cost per bit.
Package is the First to Accommodate System Design Considerations
The Dual In-line Package (DIP) format significantly eases printed circuit board layout and reduces computer assembly cost.
Mainframe Computers Employ ICs
Large computer manufacturers announce machines based on custom and special purpose integrated circuits.
"Moore's Law" Predicts the Future of Integrated Circuits
Fairchild's Director of R & D predicts the rate of increase of transistor density on an integrated circuit and establishes a yardstick for technology progress.
Computer Aided Design Tools Developed for ICs
IBM engineers pioneer computer-aided electronic design automation tools for reducing errors and speeding design time.
Semiconductor RAMs Serve High-speed Storage Needs
Bipolar RAMs enter the computer market for high-performance scratchpad and cache memory applications.
Application Specific Integrated Circuits employ Computer-Aided Design
Automated design tools reduce the development engineering time to design and deliver complex custom integrated circuits.
Turnkey Equipment Suppliers Change Industry Dynamics
Third-party vendors develop specialized knowledge of semiconductor fabrication and emerge as vendors of process technology and turnkey manufacturing facilities.
Silicon Gate Technology Developed for ICs
Federico Faggin and Tom Klein improve the reliability, packing density, and speed of MOS ICs with a silicon-gate structure. Faggin designs the first commercial silicon-gate IC – the Fairchild 3708.
Dedicated Current Source IC Integrates a Data Conversion Function
The precision manufacturing requirements of combining analog and digital capability on one chip made them one of the last product areas to yield to monolithic solutions.
Schottky-Barrier Diode Doubles the Speed of TTL Memory & Logic
Design innovation enhances speed and lowers power consumption of the industry standard 64-bit TTL RAM architecture. Is quickly applied to new bipolar logic and memory designs.
1970s
MOS Dynamic RAM Competes with Magnetic Core Memory on Price
The Intel i1103 Dynamic RAM (DRAM) presents the first significant semiconductor challenge to magnetic cores as the primary form of computer memory.
Microprocessor Integrates CPU Function onto a Single Chip
Silicon-gate process technology and design advances squeeze computer central processing units (CPU) onto single chips.
Reusable Programmable ROM Introduces Iterative Design Flexibility
Dov Froman's ultra-violet light erasable ROM design offers an important design tool for the rapid development of microprocessor-based systems, called an erasable, programmable read-only-memory or EPROM.
Scaling of IC Process Design Rules Quantified
IBM researcher Robert Dennard's paper on process scaling on MOS memories accelerates a global race to shrink physical dimensions and manufacture ever more complex integrated circuits.
General-Purpose Microcontroller Family is Announced
A single-chip calculator design emerges as the TMS 1000 micro-control unit or MCU, a concept that spawned families of general-purpose digital workhorses that power the tools and toys of the developed world.
Digital Watch is First System-On-Chip Integrated Circuit
The Microma liquid crystal display (LCD) digital watch is the first product to integrate a complete electronic system onto a single silicon chip, called a System-On-Chip or SOC.
PAL User-Programmable Logic Devices Introduced
John Birkner and H. T. Chua of Monolithic Memories develop easy-to-use programmable array logic (PAL) devices and tools for fast prototyping custom logic functions.
Single Chip Digital Signal Processor Introduced
Bell Labs' single-chip DSP-1 Digital Signal Processor device architecture is optimized for electronic switching systems.